Instruction Sets¶
Instruction¶
정의 ***¶
컴퓨터가 수행해야할 명령을 나타내는 bit pattern.
CPU에서 control unit이 이를 해석하여 이에 해당하는 제어신호를 보내게 됨.
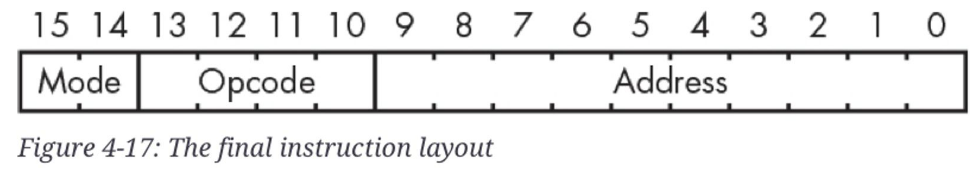
일반적으로 instruction은
- (addressing) mode
- operation code (opcode)
- address
로 구성됨 (Single-address instruction layout).
mode- addressing mode를 가르킴. 간단히 말하면 3가지의 다른 addressing mode가 존재함.
opcode- 수행할 명령어를 나타내는 code.
address- 현재 수행할 instruction과 관련된 data들이 놓인 memory location 혹은 data 그 자체, 또는 memory location이 놓여있는 memory location. (addressing mode에 따라 다름)
Single-address instruction layout은 ALU에서의 결과가 accumulator에 저장되고 해당 accumulator를 operand로 사용하는 형태.
- 한번에 하나의 memory location에 접근하면 되며, 적은 크기의 instruction으로 수행가능하다는 장점을 가짐.
Addressing Mode (주소지정 모드)¶
여기서 다루는 addressing mode는 absolute addressing에 해당함.
후에 다루는relative addressing도 존재.
instruction에서 memory location을 가르키는 방법은 다음과 같은 3가지로 나뉜다.
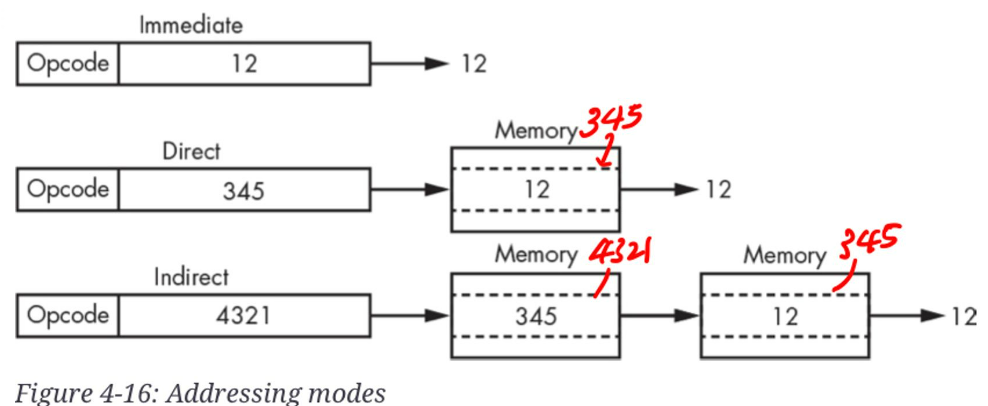
immediate mode addressing¶
- instruction에 address가 아닌 실제 값이 들어가 있는 경우임.
- 작은 크기(bit)의 상수값을 이용하는 경우 사용되며 가장 속도가 빠른 방식.
direct addressing¶
- instruction에 포함된 address가 reference하는 곳(memory location)에 instruction이 사용할 value(값)이 있음.
indirect addressing¶
- instruction에 포함된 address가 가르키는 곳에 또 address가 들어 있음.
- 즉, instruction에 포함된 address가 reference하고 있는 memory location에 가서 값을 가져오는게 아니고,
- 해당 memory location의 값이 또 address이기 때문에 다시 해당 address가 reference하고 있는 memory location으로 가서 값을 가져옴.
instruction의 크기를 늘리지 않고도 보다 큰 용량의 memory로 확장할 수 있음.
단, 2번에 걸쳐 memory에 접근하므로 가장 느림.
absolute addressing은 주소 0을 기준으로 address를 나타내지만,
relative addressing은 현재 주소를 기반으로 상대적인 값을 통해 address를 나타낸다.
Condition Code Instructions.¶
condition code register를 직접 다루는 instruction을 가르킴.
cca instruction
- Condition Code register → Accumulator
- condition code register의 저장된 값을 accumulator로 copy.
acc instruction
- Accumulator → Condition Code register
Branching (분기, 분기명령)¶
일반적으로 하나의 instruction이 수행되고 나면, PC register가 가르키고 있는 instruction을 수행하게 되고, 해당 다음 instruction을 수행하기 전 PC는 하나가 증가하게 됨. 이 같은 경우, 메모리에 저장된 instruction들을 순서대로 수행하게 된다.
하지만 프로그램이 항상 순서대로만 수행되는 게 아닌 특정 조건에 따라 다른 순서로 수행해야 하는 경우도 있기 때문에 이를 위한 branching 명령어 가 존재함.
이들은 PC register의 값을 직접 변경하여, instruction들의 수행순서를 바꾸게 함. 대표적인 Branch instruction의 종류와 이에 해당하는 조건은 다음과 같음.
| Code | Mnemonic | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 000 | bra | branch always. |
| 001 | bov | branch if the O (overflow) condition code bit is set. |
| 010 | beq | branch if the Z (zero) condition code bit is set. |
| 011 | bne | branch if the Z condition code bit is not set. |
| 100 | blt | branch if N (negative) is set and Z is clear. |
| 101 | ble | branch if N or Z is set. |
| 110 | bgt | branch if N is clear and Z is clear. |
| 111 | bge | branch if N is clear or Z is set. |
- condition code register의 해당하는 bit에 대한 조건을 만족하면 branching.
위에서 살펴본 것처럼 조건에 의해서 branching하지 않고, program counter register의 값을 명시적으로 그냥 바꾸는 등의 동작을 수행하는 instruction도 존재함.
pca: 현재 program counter register의 값을 accumulator로 copy.apc: 현재 accumulator의 값을 program counter register로 copy.
Final Instruction Set¶
16bit 기준 single address instruction layout은 다음과 같음.
| Opcode | Direct (00) | Indirect (01) | Immediate (10) | None (11) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 | load | load | load | |
| 0001 | and | and | and | set |
| 0010 | or | or | or | not |
| 0011 | xor | xor | xor | neg |
| 0100 | add | add | add | shl |
| 0101 | sub | sub | sub | shr |
| 0110 | cmp | cmp | cmp | acc |
| 0111 | store | store | cca | |
| 1000 | bra | bra | bra | apc |
| 1001 | bov | bov | bov | pca |
| 1010 | beq | beq | beq | |
| 1011 | bne | bne | bne | |
| 1100 | blt | blt | blt | |
| 1101 | ble | ble | ble | |
| 1110 | bgt | bgt | bgt | |
| 1111 | bge | bge | bge |
shl,shr는 operation에서 사용하지 않는 하위 4비트를 이용하여 얼마만큼 쉬프트할지를 지정함.
program과 instruction set ***¶
우리가 만드는 program은 결국 위와 같은 instruction들의 list임.
- 사람이 알기 쉬운 high level programming language로 프로그래밍을 하여 작성된 source code 는 위에 나열된 instruction들의 list로 변경됨.
- 해당 instruction의 list는 정해진 bit size의 bit-pattern들의 묶음임.